- Curved Lithium Polymer battery
- Fast Charge Polymer Battery
- Flexible Polymer Lithium Battery
- Ultra-thin Polymer Battery
/ Blog / Battery Knowledge /
Understanding Export Inspection and Supervision Requirements for Lithium Batteries
23 Nov, 2023
By hoppt
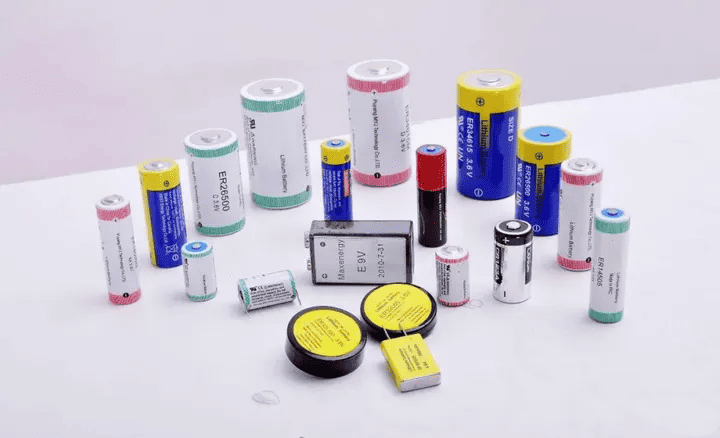

With the rapid development of electronic technology, high demands are placed on power sources for electronic devices and equipment. Lithium batteries, widely used in new energy vehicles, mobile phones, laptops, electric tools, pacemakers, backup power sources, and small household appliances, have advantageous properties like high energy density and longevity. However, their hazardous characteristics cannot be ignored.
What is a Lithium Battery? Lithium batteries, proposed by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1912 and further researched in the 1970s by M. S. Whittingham, are batteries that use lithium metal or lithium alloy as anodes/cathodes with a non-aqueous electrolyte solution. The reactive chemical nature of lithium metal demands high environmental standards for processing, storage, and usage.
Classification of Lithium Batteries:
- Lithium Metal Batteries: Typically use manganese dioxide as the cathode material and metallic lithium or its alloy as the anode material with a non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Generally use lithium metal oxide as the cathode material and graphite as the anode material with a non-aqueous electrolyte.

Are Lithium Batteries Dangerous Goods? As per the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and other international regulations, lithium batteries may fall under Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods (miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles, including environmentally hazardous substances), with UN numbers including UN3090, UN3091, UN3480, and UN3481.
Do Lithium Batteries Require Dangerous Goods Packaging? Based on the capacity of the lithium battery, it must be determined whether it requires dangerous goods packaging, as stipulated by the United Nations.
Batteries requiring such packaging include:
- Lithium metal or alloy batteries with more than 1 gram of lithium content, or battery packs with more than 2 grams in total.
- Lithium-ion batteries with watt-hour ratings exceeding 20Wh, or battery packs exceeding 100Wh.
Pre-shipment Testing Requirements for Lithium Batteries: Before transportation, lithium batteries must pass a series of tests as required by the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, including altitude simulation, temperature cycling, vibration, impact, external short circuit, and forced discharge tests, to ensure safe transportation.
What Procedures are Needed for Exporting Lithium Batteries? As per the "People's Republic of China Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law," Article 17, enterprises producing packaging containers for exporting dangerous goods must apply for performance appraisal of the packaging containers. Dangerous goods in unapproved packaging containers are not allowed for export.
For lithium batteries that require dangerous goods packaging, an application must be made to the local customs for an export dangerous goods packaging performance inspection and usage appraisal to obtain the "Outbound Cargo Transportation Packaging Performance Inspection Result Sheet" and "Outbound Dangerous Goods Transportation Packaging Usage Appraisal Result Sheet." Simplification of documentation can be done as per relevant regulations like the "Announcement on the Electronization of Inspection and Quarantine Documents" (Customs Administration Announcement No. 90 of 2018).



